Tumor Vascular Intervention
 2021-11-25
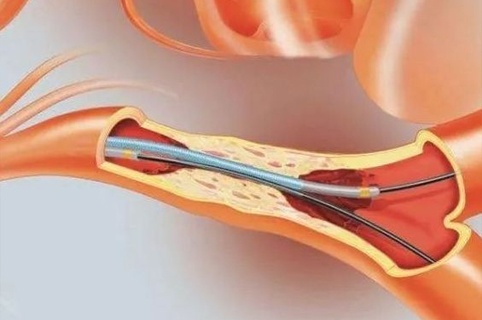
2021-11-25 Tumor interventional technology includes transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), thermal ablation, nanoknife, seed implantation and other interventional treatment technologies and combined therapies. TACE refers to the selective or superselective insertion of catheters into the blood supply of tumors. After the target artery, an appropriate amount of embolic agent is injected at an appropriate speed to occlude the target artery and cause ischemic necrosis of the tumor tissue. Embolization with anticancer drugs or drugs combined with microparticles and microspheres can play the role of chemotherapeutic embolization.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a blood-rich malignant tumor originating from liver cells, and 90% of the blood supply comes from the hepatic artery. Liver metastases reach a diameter of more than 2-2.5mm and are completely supplied by the hepatic artery. In the treatment of primary liver cancer HCC, TACE technology has become the first major treatment method, and the treatment of liver cancer has gradually formed a local combined system treatment centered on TACE. In the future, as one of the important methods in tumor interventional therapy, it uses embolic materials to block the blood vessels of tumors, causing ischemic necrosis of tumor tissues. In addition to "blocking tumors", interventional embolization microspheres can also use anti-cancer drugs or drugs combined with microparticles and microspheres for embolization, which can play a role in chemotherapeutic embolization and achieve a "two-pronged" therapeutic effect.
After years of development, TACE technology is divided into three main technologies: ① traditional hepatic artery chemoembolization (c-TACE); ② drug-loaded microsphere intervention (D-TACE) ③ transcatheter arterial radiotherapy embolization (TARE).
c-TACE is a conventional transcatheter arterial embolization. The embolic materials used are mainly super-liquefied lipiodol, gelatin sponge particles, PVA particles, and blank microspheres. Usually one or several cytotoxic drugs (including doxorubicin and epirubicin) are mixed with an embolic agent, and then the embolic agent is used to block the blood supply artery of the tumor. The principle of tumor treatment is to block the blood supply of the tumor. Arteries, to achieve the effect of inducing tumor ischemic necrosis.
The biggest difference between D-TACE and traditional c-TACE is the embolic material. The embolic material of D-TACE is drug-loaded microspheres that can absorb and carry chemotherapeutic drugs. Unlike c-TACE's treatment method, D-TACE has a dual function in killing cancer cells. On the one hand, it can embolize the blood supply arteries of liver tumors. On the other hand, it can allow chemotherapeutic drugs to act on the inside of the tumor at a higher concentration and for a longer time. Realize the effect of 1+1>2 clinically.
TARE and TACE are both injected through the hepatic artery through a catheter, but the interventional material of TARE is microspheres coated with metal isotopes. The implantation method is the same as that of D-TACE. After the radioactive microspheres are accurately implanted near the tumor, they are released. Short-distance and high-dose beta rays kill tumor cells. However, the radioactive source of TARE is radioactive particles, which has a half-life and has high requirements for construction, transportation, storage and surgery.
As the incidence of liver cancer continues to rise, it will promote the expansion of the TACE treatment market for liver cancer. The penetration rate of TACE surgery in China is about 50%. With the improvement of awareness and market education, the penetration rate of TACE is expected to increase to 70%-80% in the future. Currently in the TACE market, emerging technologies including D-TACE and TARE account for only about 10%. As new technologies continue to be accepted, it will further promote the growth of tumor embolism interventional therapy. The application of TACE technology is expanding. In addition to liver cancer, TACE is expected to be used in all solid organ tumors such as breast cancer, lung cancer, uterine fibroids, and non-tumor fields such as prostate hyperplasia. TACE technology expands more application scenarios for the development of broad-spectrum drug-loaded microspheres.